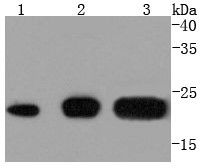
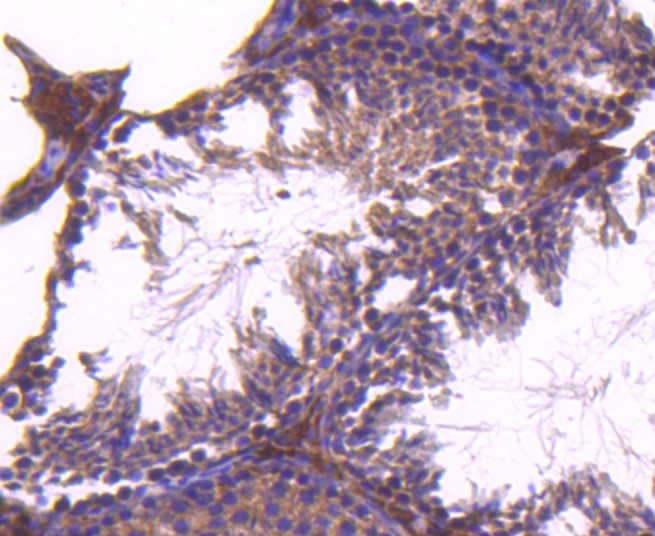
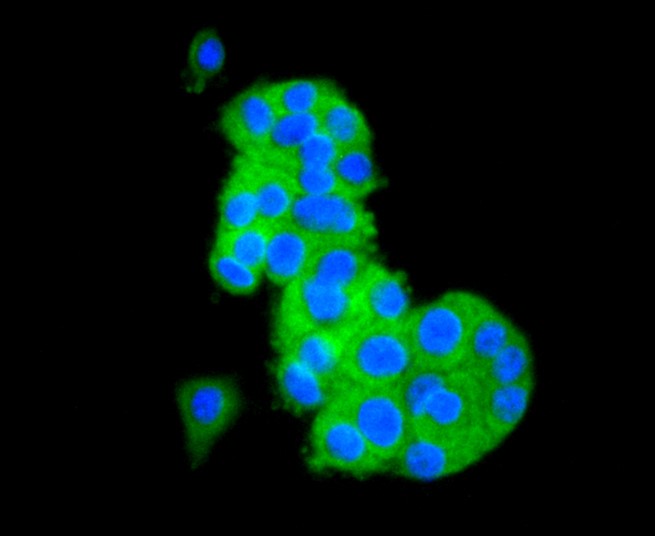
Background:
CD81 belongs to the tetraspanin family, which is characterized by four transmembrane domains, one short extracellular domain (ECL1), and one long extracellular domain (ECL2). Tetraspanins interact with a variety of cell surface proteins and intracellular signaling molecules in specialized tetraspanin enriched microdomains (TEMs) where they mediate a range of processes including adhesion, motility, membrane organization, and signal transduction. CD81, like other tetraspanins, is enriched in exosomes. Many research studies demonstrate a role for CD81 in lymphocyte signaling. CD81 is also a well-characterized receptor for Hepatitis C Virus and facilitates the entry of the virus into target cells.
UniProt ID: P35762