Ni-NTA Superflow sepharose is a nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) modified Superflow 6 support charged with divalent nickel (Ni+2) designed for FPLC purification of poly-histidine-tagged proteins.
Ni-NTA Superflow sepharose is a highly crosslinked, durable resin that does not compress at flow rates used for medium- or large-scale FPLC purifications. The resin holds up well to a variety of chemicals and pH values, and is compatible with common clean-in-place procedures. Compared to cobalt and other ligands used for immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), nickel provides greater capacity for His-tagged protein purification.
Ni-NTA Superflow sepharose exhibits a high dynamic binding capacity across a range of flow rates, making it an excellent choice for larger scale purifications.
Ni-NTA Agarose Resin 6FF for His tagged Protein Purification
Catalog number :P3403
- Overview
- Description
- Ni-NTA Agarose Resin 6FF for His tagged Protein Purification
- Tested applications
- immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) for His tagged Protein Purification
- Product Picture
- Properties
- Storage instruction
- 2 to 8°C,
Up to 25 times
- Conjugation
- Metal: ≥15μmol Ni2+/mL resin
- Structure Image
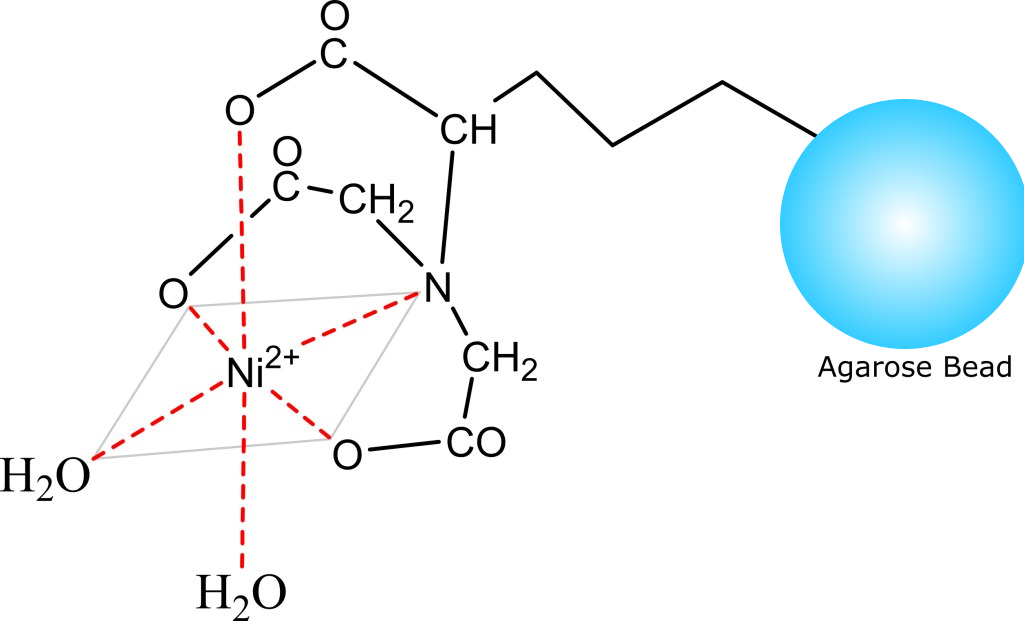
- Beads Diameter
- 90 µm (60 to 160μm)
- Binding Capacity
- Dynamic: approx. 40 mg 6xHis-GFP/mL settled resin
- Matrix
- Superflow Resin, highly crosslinked 6% agarose beads
- Chemical stability
- 1M acetic acid pH 2, 1% SDS pH 7, 70% ethanol for ≥1 week at 37°C; 8M urea, 10mM DTT, 5mM TCEP for ≥2 hours at 22°C
- pH stability
- pH 3 to 9 for ≥1 week at 4°CpH 2 to 3 or 9 to 12 for ≥ 2 hours at 22°C
- Storage buffer
- 20% ethanol
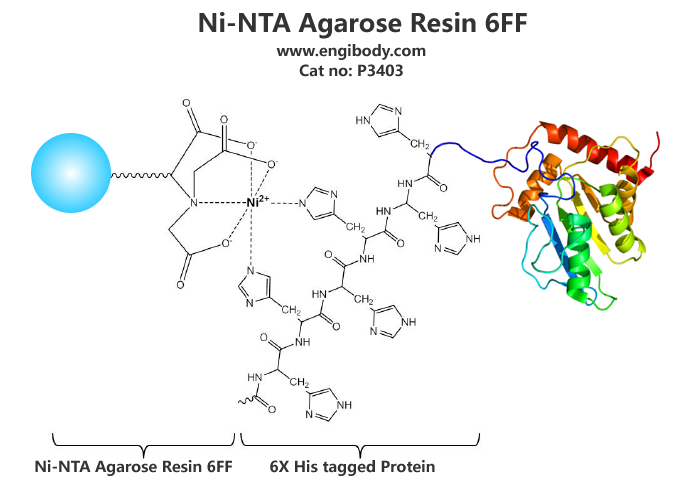
- Applications
- Application Image
- Highlights
- High capacity – binds greater than 40mg of His-tagged GFP per mL of resinHigh purity – provides greater than 85% purity of eluted fractions when used to purify from lysatesVersatile – can be used to purify proteins under native and denaturing conditionsCompatible – maintains function in a wide variety of chemicals and pH conditionsCost effective – competitively priced resin is stable through multiple cycles of cleaning and reuse
- Work Flow Image
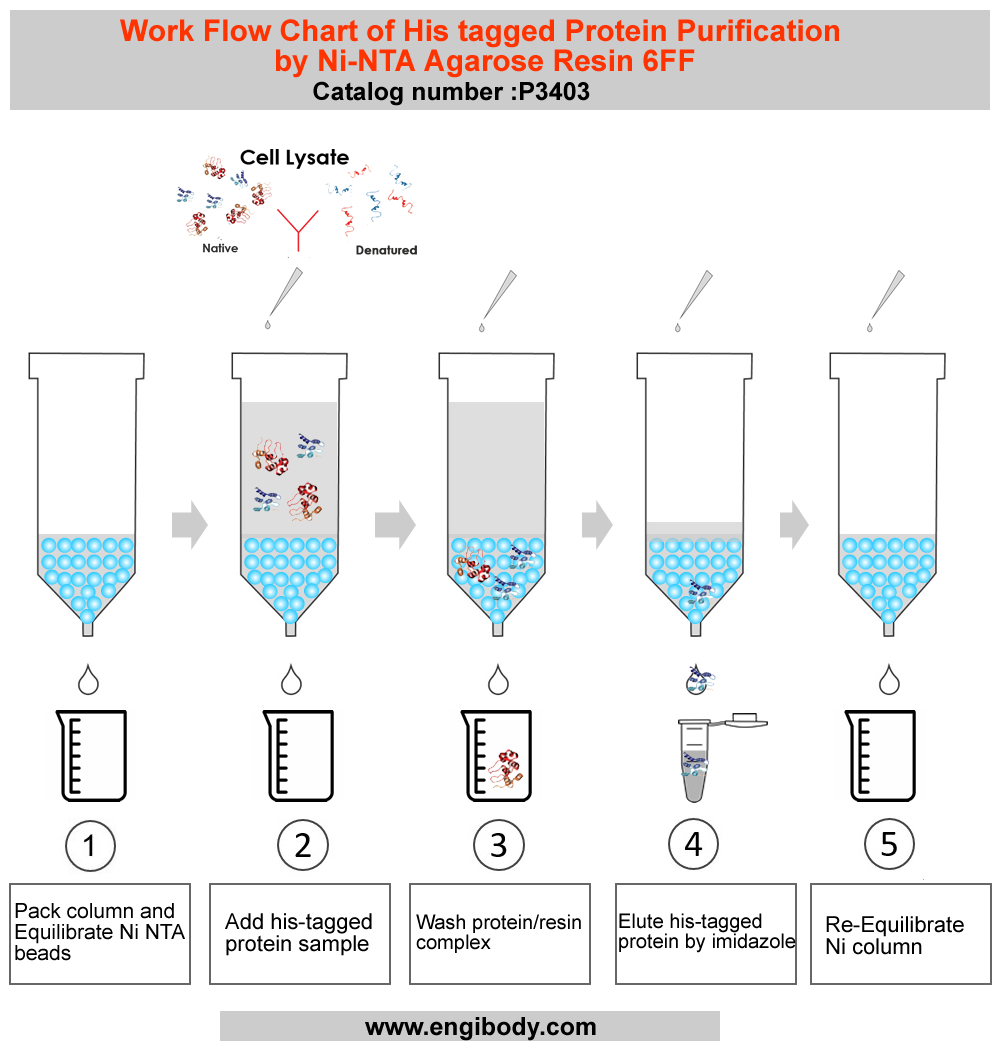
- Protocols
Purification Protocol
Purification of soluble 6×his-tagged proteins under native conditions
1. Buffer PreparationWater and chemicals used for buffer preparation should be of high purity. It is recommended filtering the buffers by passing them through a 0.45 µm filter before use.Equilibration Buffer (also named Lysis/Equilibration Buffer, LE buffer): 50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, pH 8.0Wash Buffer: 50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, pH 8.0Elution buffer: 50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, pH 8.02. Sample Preparation2.1. For protein expressed in E. coli or yeast cytoplasm.1) Harvest cells from a 50 mL culture by centrifugation at 4°C (e.g., 5,000 rpm for 15 minutes).2) Resuspend the cells in 10 mL of Lysis/Equilibration buffer (LE buffer) with appropriate amount of PMSF (Final working concentration can be 1mM) and add lysozyme (Final working concentration is 0.2-0.4 mg/mL), or other protease inhibitors cocktail added (PIC cannot contain EDTA or EGTA).Note: The inhibitors must have no effect on the ability of the Ni2+ resin.3) Sonicate the solution on ice using 180 one-second bursts at high intensity with a three-second cooling period until the bacterial liquid is clear.Optional: If the lysate is too viscous, add RNase A (10 µg/mL) and DNase I (5 µg/mL) and incubate on ice for 10-15 minutes.4) Centrifuge the lysate at 12,000 rpm for 15-25 minutes at 4°C to pellet the cellular debris. Take the supernatant and store it in a new centrifuge tube. Apply the supernatant onto the Ni2+ column in next steps.2.2. For proteins secreted into culture medium by yeast, insect, or mammalian expression systems.1) If the culture supernatant does not contain EDTA, histidine, or any other reducing agents that might affect the Ni2+ column, it can be applied directly to the column. Otherwise, perform the following procedures.2) Dialyze the sample against 1 × PBS before applying it onto the column.3) For large volume of supernatant, concentrate the proteins by ammonium sulphate precipitation, dialyze the dissolved protein solution against 1 × PBS, and then apply the solution onto the Ni2+ column.3. Pack Column and Equilibrate Ni2+ Resin.1). Mix the slurry by gently inverting the bottle several times to completely suspend the resin.2). Transfer an appropriate volume (2 - 4mL) of the slurry to the column. Allow the resin to settle down and the storage buffer to drain from the column.3). Equilibrate the column with 5 × bed volumes of Equilibration buffer (LE buffer) until A280 is stable.4. Native 6×his-tagged Proteins Purification1). Add the clear sample containing target 6×his -tagged protein onto the equilibrated gravity column, keep the sample in column for at least 2 min, ensure that the sample fully binds with the resin, and collect the flowthrough with a flow-rate of 0.5 - 1 mL per minute, then add the flowthrough onto the column again, repeat the previous operation, this can increase the binding efficiency.2). Wash the column with 10 - 15 × bed volumes of Wash buffer until A280 is stable at the flow-rate of 1 mL per minute. Remove non-specific adsorbed proteins. Collect the wash fractions.3). Use 5-10 × bed volume of Elution buffer to elute, collect in fractions, collect one tube for each bed volume, and test separately, which can not only ensure that all binding target proteins are eluted, but also obtain high-purity and high-concentration proteins.4). Dialyze it against 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) or 1 × PBS (pH 7.4) according to the specific application of the target protein.5. Re-Equilibration of Resin3 × bed volumes of Equilibration Buffer and 5 × bed volumes of deionized water are used to equilibrate the resin in the order. Store the resin in 3 × bed volumes of 1×PBS (20% ethanol) at 4°C-30°C to prevent bacterial pollution of the resin.Purification of 6×histidine-tagged proteins from E. coli under denaturing conditions
This protocol is for target proteins that are expressed mainly in inclusion bodies.
1. Buffer PreparationWater and chemicals used for buffer preparation should be of high purity. It is recommended filtering the buffers by passing them through a 0.45 µm filter before use.Lysis/Equilibration Buffer (LE buffer) for Inclusion Body: 100 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM Tris.Cl, 8 M urea, pH 8.0Wash Buffer for Inclusion Body: 100 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM Tris.Cl, 10 mM Imidazole, 8 M urea, pH 8.0Elution buffer for Inclusion Body: 100 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM Tris.Cl, 250 mM Imidazole, 8 M urea, pH 8.02. Disrupting Bacteria and Solubilization of Inclusion Bodies1). Resuspend the bacteria pellet in cold (4°C) 1× PBS (about 10 mL per mL of pellet), and disrupt bacteria by sonication as described above.2). Collect inclusion bodies by centrifuging the lysate at 12,000 rpm for 10-20 minutes at 4°C. Wash inclusion bodies with 1× PBS several times if necessary.3). Solubilize the inclusion bodies in LE buffer for Inclusion Body (about 10 mL/mL bacterial pellet), and incubate for 30-60 minutes at room temperature. Homogenization or sonication may be necessary to fully solubilize the pellet.4). Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 30 minutes to remove any remaining insoluble material.Attention:If the inclusion body protein still cannot be dissolved, then Guanidine HCl (final working concentration is 6mM) can be added into LE buffer for Inclusion Body, and the obtained protein solution must be dialyzed into LE buffer for Inclusion Body, then the protein solution can be added onto the column for purification. because Guanidine HCl is harmful to Ni2+ column.3. Denatured 6×his-tagged Proteins Purification1). Carefully transfer supernatant to a clean tube without disturbing the pellet.2). Add the clear supernatant containing target 6×his -tagged protein onto the equilibrated gravity Ni2+ column pre-equilibrated with LE Buffer for Inclusion Body, keep the sample in column for at least 2 min, ensure that the sample fully binds with the resin, and collect the flowthrough with a flow-rate of 0.5 - 1 mL per minute, then add the flowthrough onto the column again, repeat the previous operation, this can increase the binding efficiency.3). Wash the column with 10 - 15 × bed volumes of Wash buffer for Inclusion Body until A280 is stable at the flow-rate of 1 mL per minute. Remove non-specific adsorbed proteins. Collect the wash fractions.4). Use 5-10 × bed volume of Elution buffer for Inclusion Body to elute, collect in fractions, collect one tube for each bed volume, and test separately, which can not only ensure that all binding target proteins are eluted, but also obtain high-purity and high-concentration proteins.5). Dialyze it against 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) or 1 × PBS (pH 7.4) according to the specific application of the target protein.Note: The protocol recommended here is to purify target protein from inclusion bodies, thus the eluted protein from this process may need to be refolded to obtain the active and soluble protein.4. Re-Equilibration of Resin3 × bed volumes of 1×PBS and 5 × bed volumes of deionized water are used to equilibrate the resin in the order. Store the resin in 3 × bed volumes of 1×PBS (20% ethanol) at 4°C-30°C to prevent bacterial pollution of the resin.After using the resin for several times, if the binding capacity drops very much or the color of the resin has changed significantly, then nickel ion regeneration of the resin can be performed.
Regeneration of Ni2+ Column (Optional Step)For complete regeneration, wash the resin with the following solutions:1). 5 × bed volumes of deionized water2). 5 × bed volumes of 100 mM EDTA (pH 8)3). 10 × bed volumes of deionized water4). 5 × bed volumes of 0.5M NaOH5). 10 × bed volumes of deionized water6). 5 × bed volumes of 100 mM NiSO47). 10 × bed volumes of deionized water8). For long-term storage, the resin should be stored in 1×PBS containing 20% ethanol at 2 - 8°C.
Related Products
Reviews
loading...