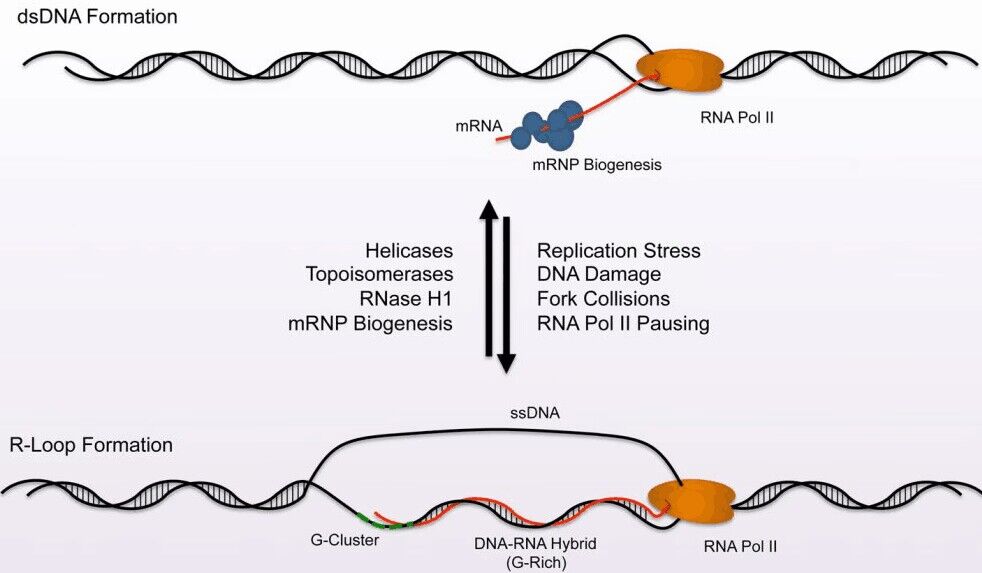
R-loops are local RNA-DNA hybrid sequences, generally formed by a nascent G-rich transcript hybridizing with the DNA template strand and thereby leaving the non-template DNA single stranded. These structures were first described in vitro in 1976 and about 20 years ago in prokaryotes having a mutation in the Topoisomerase I gene. R-loops were initially considered as a by-product of transcription, but during the past decade very important functions of R-loops in transcription, genomic stability and a variety of diseases emerged. The persistence of R-loops can result in the accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), leading to DNA rearrangements and genome instability.
Anti-DNA:RNA Hybrid [S9.6] Antibody
Catalog number :AT15001
DNA-RNA hybrids occur naturally in eukaryotic cells, Particularly at sites of high transcriptional activity.
- Overview
- Reactivity
- Species reactivity: General
- Tested applications
- DNA-RNA hybrid Immunoprecipitation (DRIP) : 5ug for 1 Reaction.
Dot blot: 1/1000.
ICC: 1/200 - 1/500.
EMSA:Optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user.
Not yet tested in other applications.
- Specificity
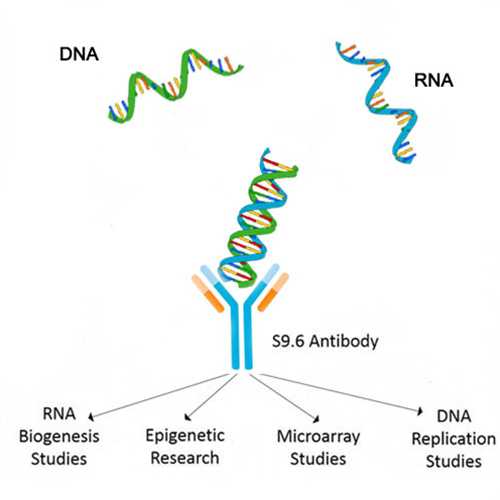
- The S9.6 monoclonal recognizes DNA-RNA hybrids (also known as R-loops) and does not bind to single or double stranded DNA (PubMed IDs: 2422282, 16614443). The antibody has high affinity for DNA-RNA hybrids but also weakly binds RNA-RNA hybrids that are AU-rich (PubMed ID: 23784994).
The specificity of the antibody appears to be determined by a combination of sequence and structural dependency since R-loop sequence affects binding affinity (PubMed ID: 28594954).
Please see our DNA-RNA-IP (DRIP) protocol for further information.
- Product Picture 1
- Product Picture 2
- Product Picture 3
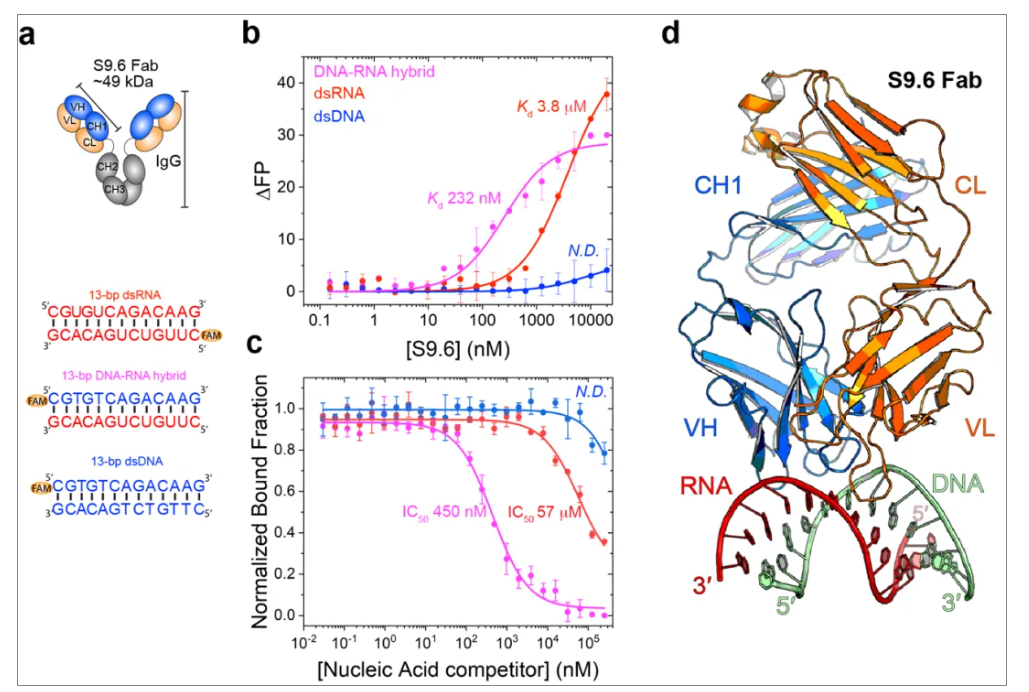
a. S9.6 Fab region and double stranded nucleic acid sequence used in the experiment.
b&c. S9.6 specifically binds to DNA-RNA hybrid duplex, while weakly binding to double stranded RNA, but not binding to double stranded DNA at all.
d. The crystal structure of the complex of S9.6 and DNA-RNA hybrid duplex.
- Properties
- Immunogen
- S9.6 ΦX174 bacteriophage-derived synthetic DNA–RNA antigen
- Clonality
- Monoclonal, Clone ID is S9.6
- Isotype
- IgG2a
- Form
- PBS with 0.02% Proclin 300 and 50% glycerol, pH 7.4
- Storage instruction
- Store at -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
- Host
- Species Immunized: Mouse(BALB/c)
- Positive Controls
- R-Loop, R-Loop (RNase A treated), R-Loop (RNase H treated), and R-Loop (DNase I treated).The pCALM3_2 vector used to generate R-loops was kindly provided by Prof. Frederic Chedin at UC Davis. The pCALM3_2 plasmid carries a 789bp fragment of the human CALM3 region that forms R-loops (PubMed ID: 31053798) cloned between T3 and T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequences. Transcription by T3 RNA polymerase leads to R-loop formation. Transcription by T7 RNA polymerase does not allow R-loop formation.
- Applications
- Highlights
- 1. Useful in the detection of R-loops
2. High specificity and affinity for DNA-RNA hybrids3. Does NOT cross-react with single-stranded DNA or double-stranded DNA4. Minor cross-reaction (~5-fold less) has been observed for AU-rich double-stranded RNA.5. High affinity binding shown for hybrids of 8, 10, 15, and 23 base pairs in length
Related Products
| Catalog number | DRIP-1001 |
Reviews
loading...