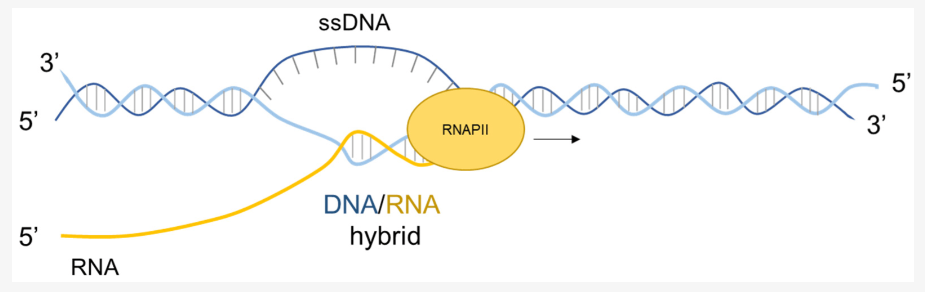
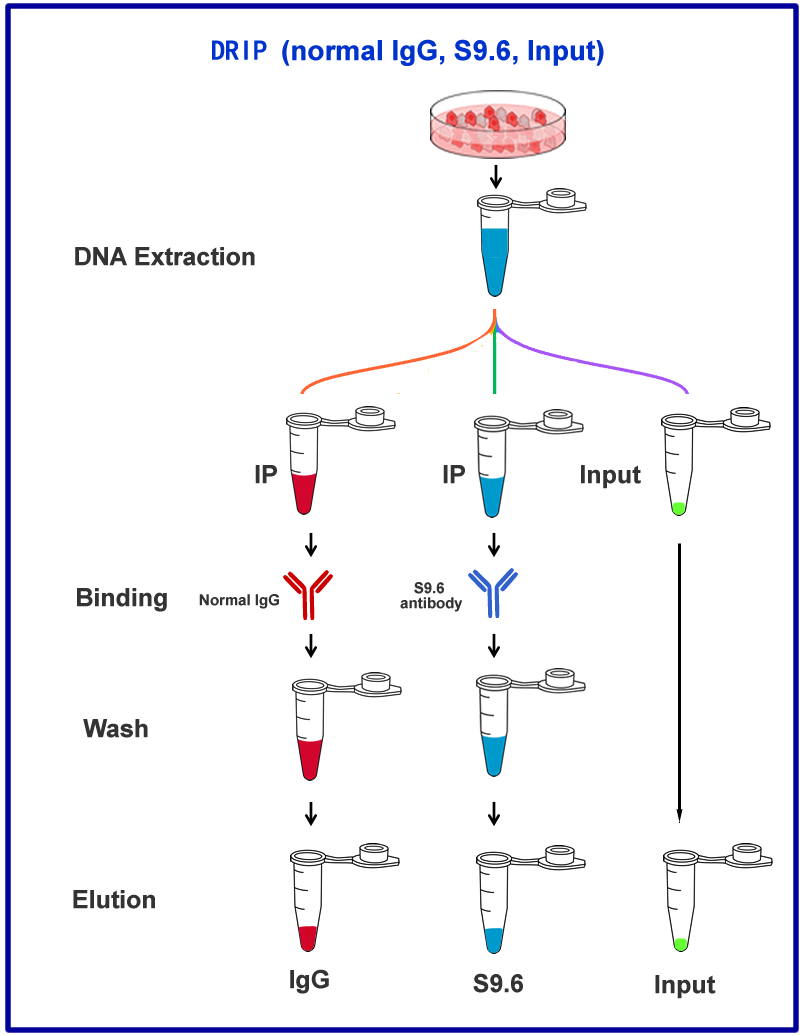
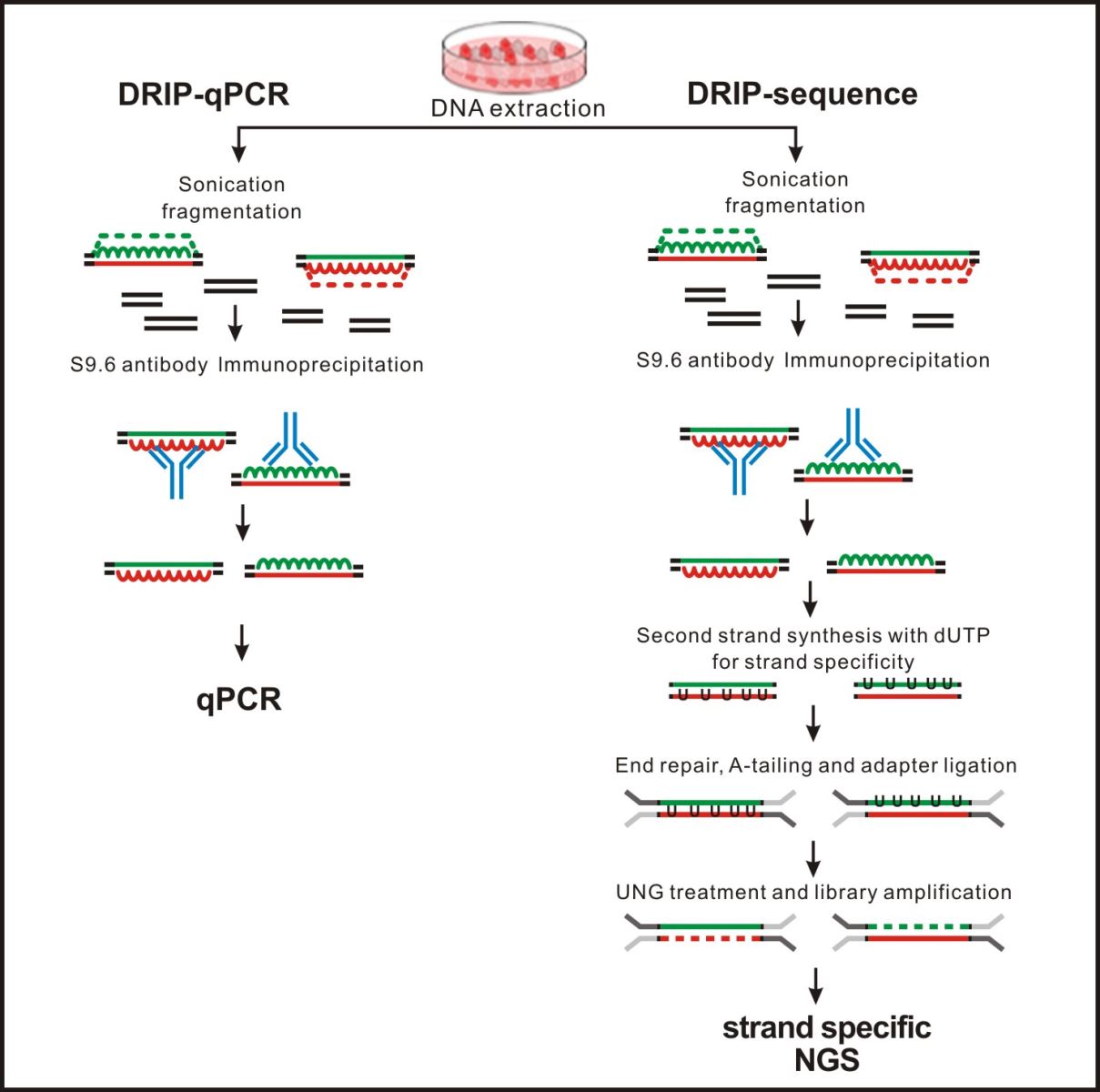
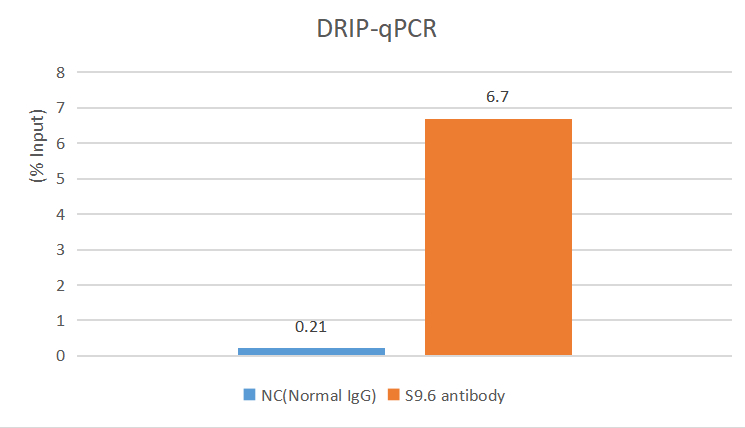
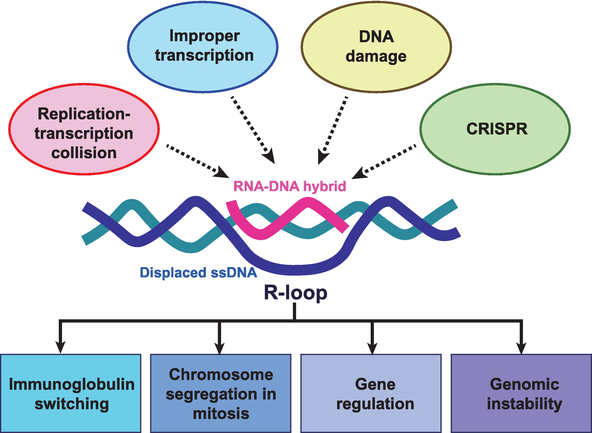
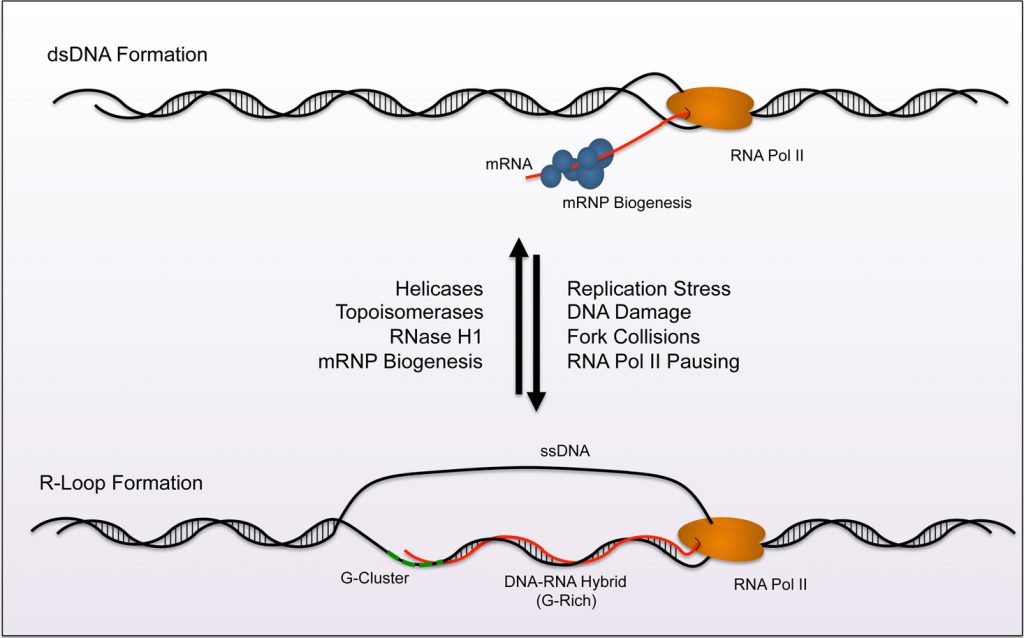
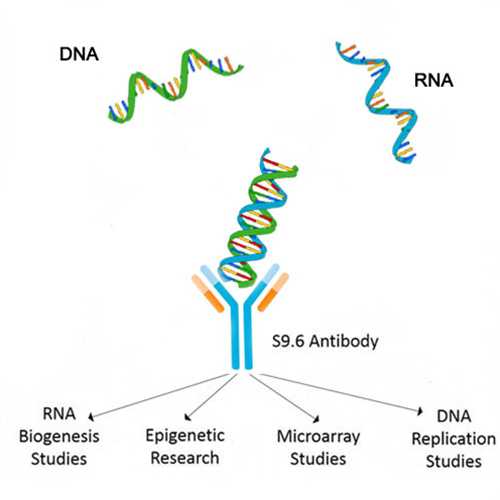
The R-loop is a special chromatin structure composed of a heterozygous RNA-DNA strand and a single stranded DNA segment.
R-loops are widely present in the genomes of bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals, accounting for approximately 5% of the mammalian genome, with most concentrated in the transcription initiation and termination regions. It plays an important role in gene transcription, DNA replication, DNA damage repair, and epigenetic modification (histone modification), and is closely related to the occurrence and development of many major diseases, making it a new research hotspot in genome biology in recent years.
Common R loops include mRNA transcription region R loop, Lnc RNA R loop, and Nami RNA enhancer R loop.