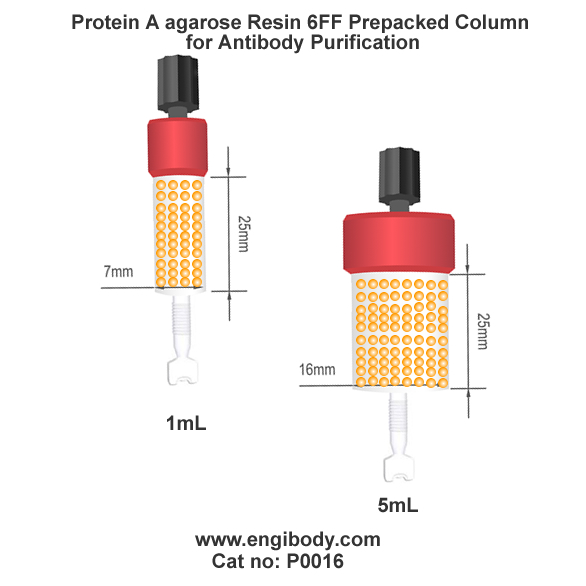
Protein A Sepharose Column consists of purified native Protein A that has been covalently immobilized at high density onto high-quality crosslinked 6% beaded sepharose. Among the many available varieties of immobilized Protein A affinity resins, this one provides the most versatile combination of chromatographic features for high yield and high purity purification of whole IgG from mammalian serum samples. The sepharose beads have physical and chemical properties suitable for many affinity purification systems. Accordingly, Protein A Sepharose Column is offered in several convenient package formats, including bottled resin slurries, three sizes of spin columns, complete purification kits, two sizes of FPLC-ready chromatography cartridges, and 96-well filter plates.
Product Details:
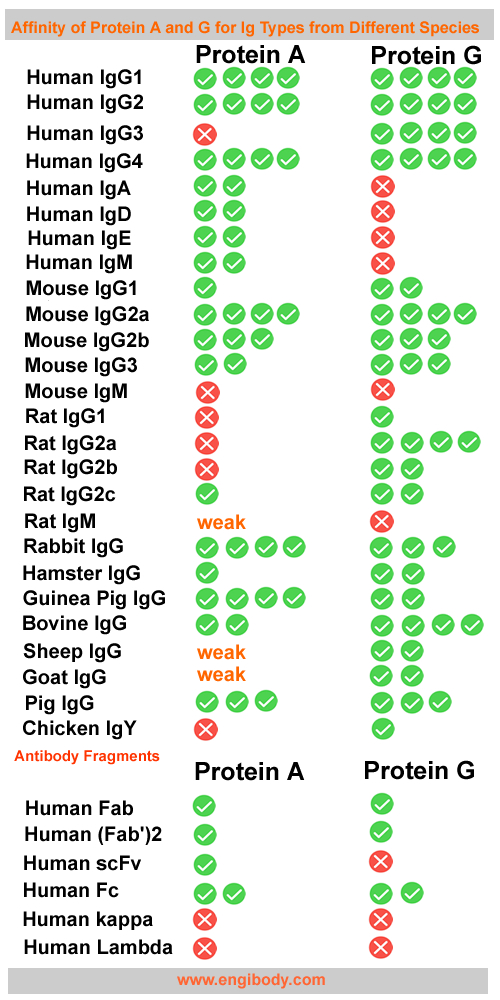
Protein A is a cell wall component produced by several strains of Staphylococcus aureus. The 46.7kDa-protein consists of a single polypeptide chain that is essentially devoid of carbohydrate. Native Protein A has contains four high-affinity (Ka = 10^8/mol) binding sites that are capable of interacting with the Fc region of IgG-class antibodies from selected mammalian species. IgG-binding function is optimal at pH 8.2, but efficient binding also occurs in neutral and physiological buffers (pH 7.0 to 7.6).
Protein A is a bacteria-derived protein that binds with high affinity and specificity to the Fc portion of antibodies, especially those of the IgG class. Compared to its alternative (Protein G), Protein A provides the highest binding capacity for subclasses of IgG from rabbits, pigs, dogs and cats. Protein A also has higher binding capacity for human IgG, except for IgG3, which it binds weakly. Protein A binds weakly to mouse IgG1 and is not recommended for most applications with that antibody isotype.
Protein A Sepharose Column provides several advantages compared to traditional methods of ligand immobilization. AminoLink Immobilization results in conjugation between sugar monomers of the agarose beads and native lysine residues on the Protein A via simple amide bonds. Unlike typical cyanogen bromide (CNBr) immobilization, the AminoLink Method does not introduce any novel chemical groups that could cause undesired nonspecific binding and produces a stable, essentially irreversible bond. The result is a high-binding-capacity resin that retains functional immobilized Protein A through multiple rounds of antibody purification.