Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay, EMSA
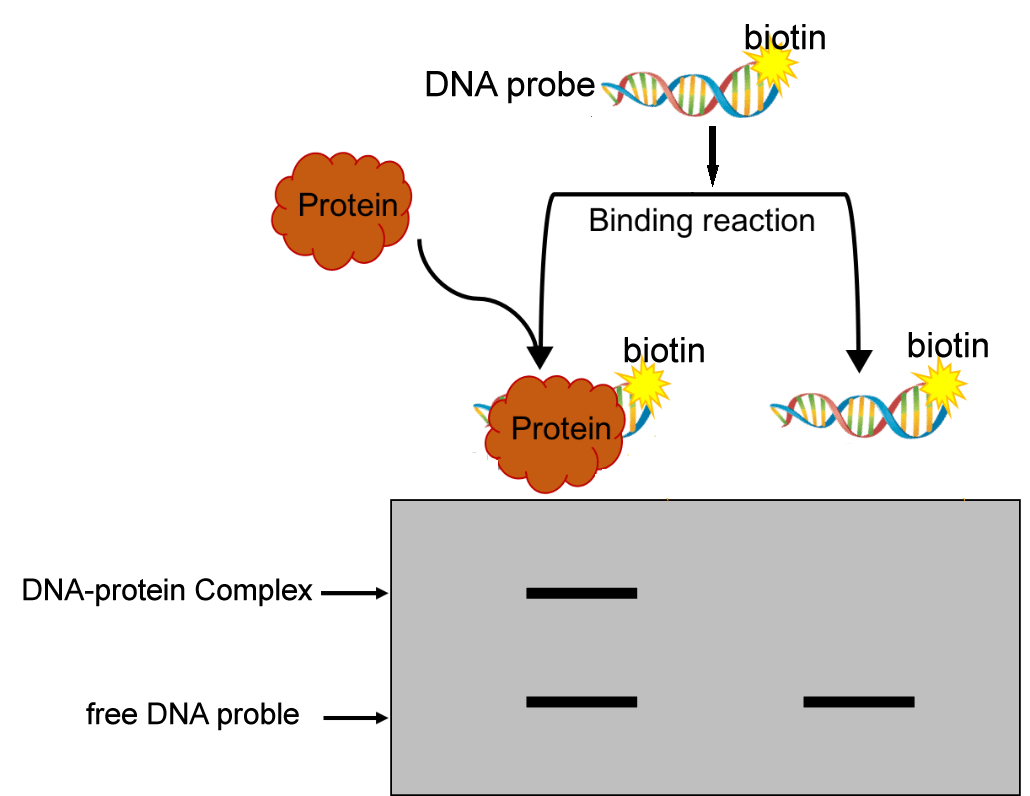
EMSA (Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay), also known as gel block experiment or electrophoretic mobility change experiment, is based on the principle that the migration of protein nucleic acid probe complex in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is slower than that of free probe. It is a technology used to detect the interaction between proteins (mainly transcription factors and transcription cofactors) and DNA fragments in vitro.
Smart-EMSA™ EMSA Kit
Catalog number :IF9501
- Overview
- Description
- Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay kit, EMSA kit
- Product Picture
- Applications
- Highlights
- This kit is suitable for adherent cells, suspended cells, animal tissues, plant tissues, and purified recombinant proteins, and is a true multi in one kit.
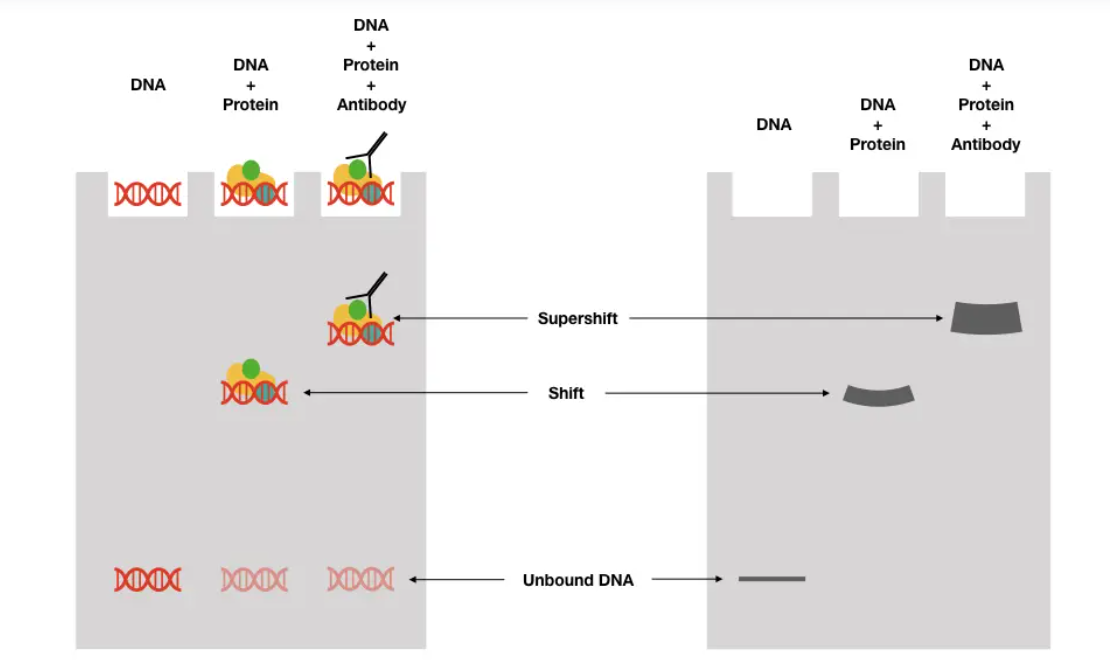
- This kit contains reagents suitable for validation type EMSA, competitive type EMSA, and SuperShift hypermigration EMSA.
- This reagent kit uses chemiluminescence detection instead of radioactive isotope detection, with high sensitivity and no harm to the health of experimental personnel.
- This manual is a comprehensive technical manual for EMSA experiments, which thoroughly analyzes the key and difficult points in EMSA experiments, and provides targeted solutions to various key and difficult problems. It also includes the basic knowledge and context of epigenetics, summarizing detailed information on the interaction between DNA and various proteins. After reading this nanny level manual, all difficulties will be easily solved, and EMSA is in control.
- Work Flow Image
- Results Display
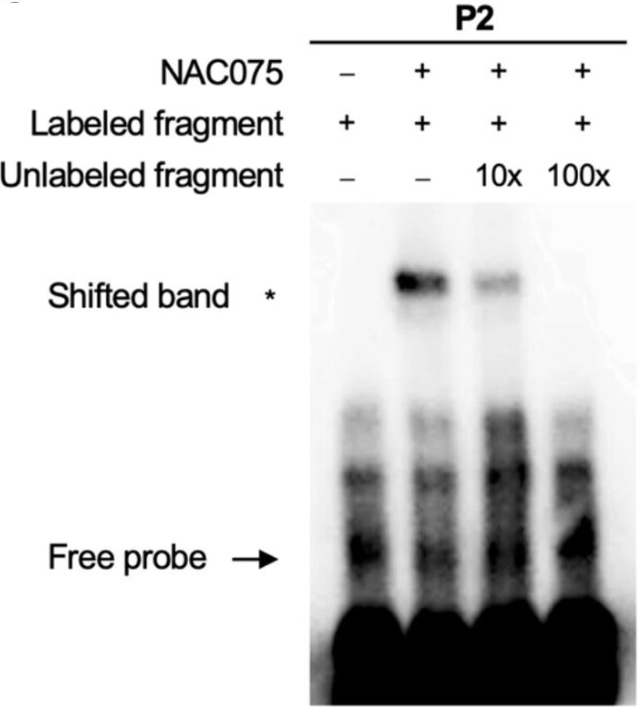
EMSA assay of the binding of NAC075 to the CAT2 promoter
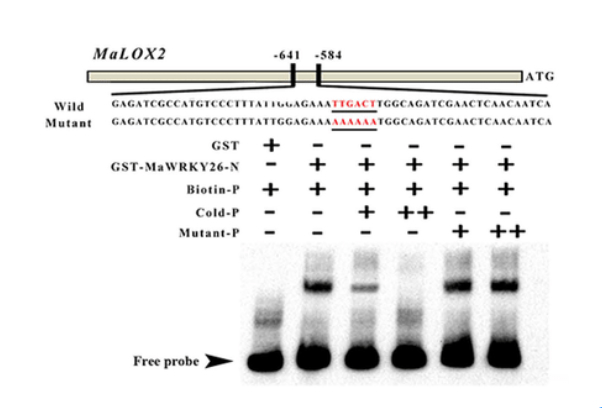
EMSA assay of the binding of MaWRKY26 to the MaLOX2 probe
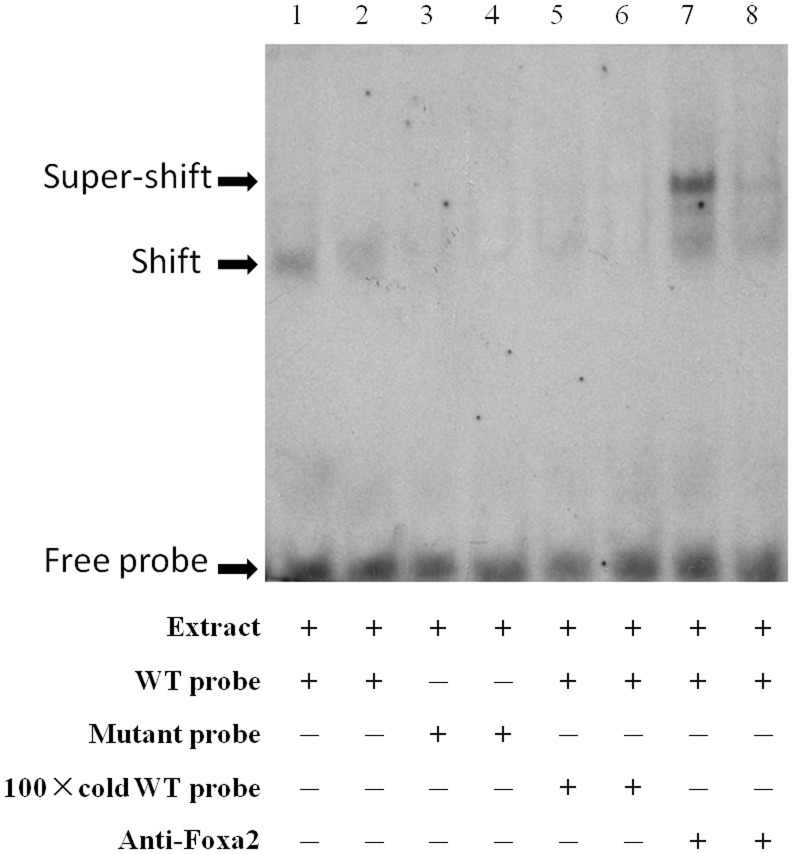
The EMSA assay showing direct binding of nuclear proteins to FTO promoter sequence using nuclear extract from HEK 293 cells (lane 1, 2). The competition assay was carried out by adding mutanted probes (lane 3, 4) or 100×unlabeled double-stranded oligonucleotide probes (lane 5, 6). The super-shift assay conducted using 20 ng anti-Foxa2 antibody (lane 7, 8). Each group was replicated with two lanes. The arrows indicate the probes, DNA-protein complexes and shift band.
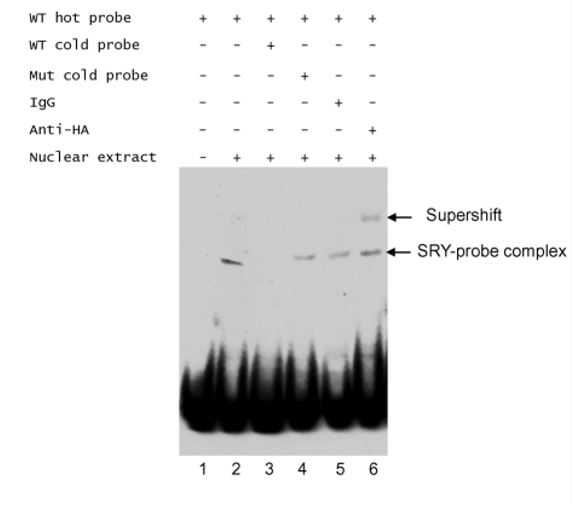
EMSA assay of the binding of SRY to the probe
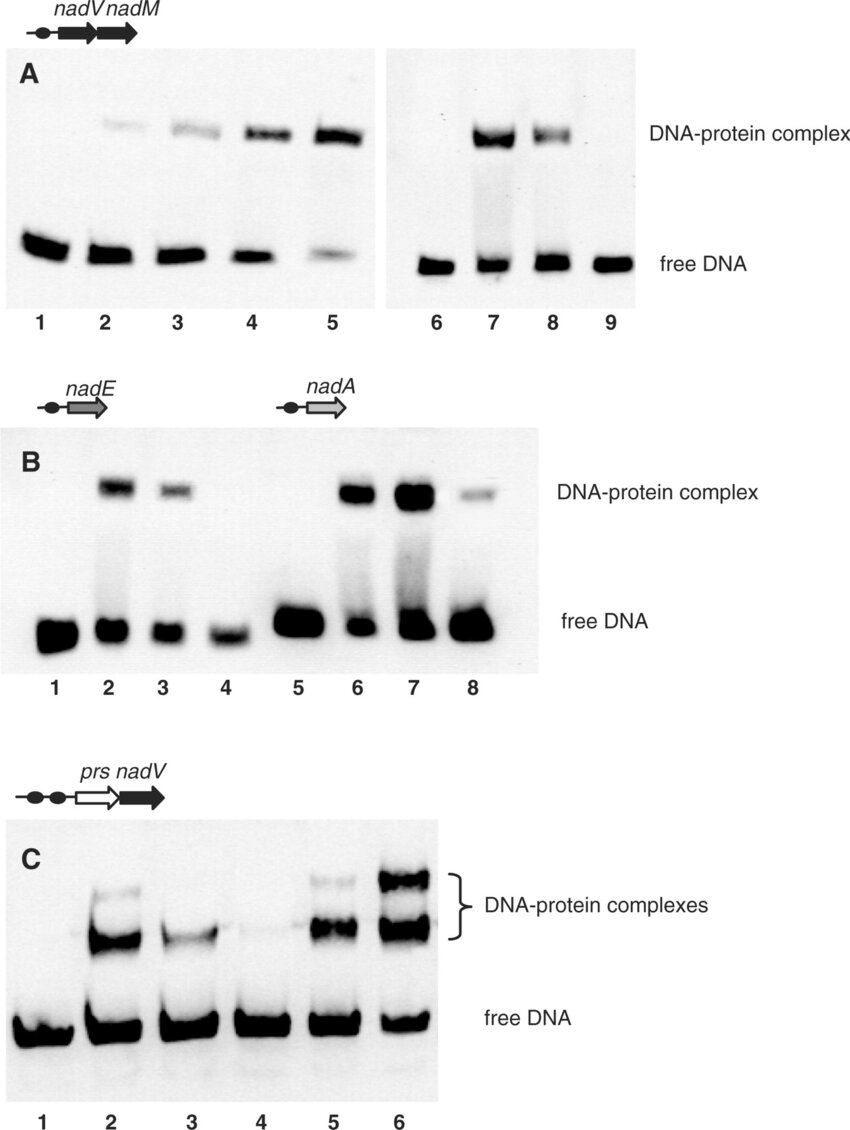
EMSA demonstrating specific NrtR binding to DNA. DNA fragments used in the assays are defined by their genomic positions and are shown as dark circles in the top of each panel. (A) EMSA with nadM-nadV DNA fragment (0.7 ng) in the absence (lane 1) and in the presence (lanes 2–5) of increasing syNrtR protein concentrations (0.25, 0.5, 1.0 and 5.0 nM, respectively). The specificity of interaction of syNrtR (2 nM) with DNA fragment (lane 7) was tested by competition with 1 μg polydC/dI (lane 8) and 140 ng unlabeled DNA fragment (lane 9). Lane 6 contains 0.7 ng of the biotylinated DNA fragment only. (B) EMSA with nadE and nadA DNA fragments in the absence (lanes 1 and 5) and in the presence of syNrtR (2 nM) (lanes 2 and 6). The specificity of interaction was tested with polydC/dI (lanes 3 and 7) and unlabeled DNA fragment (lanes 4 and 8). (C) EMSA with prs-nadV DNA fragment in the absence (lane 1) and in the presence of 2 nM soNrtR (lanes 2 and 5) and 5 nM soNrtR (lane 6). Competition assays were performed with 2 nM soNrtR in the presence of polydC/dI (lane 3) and unlabeled DNA (lane 4).
Related Products
| Catalog number | ChIP-1001 |
| Catalog number | IF9606 |
Reviews
loading...