Anti-beta Tubulin Mouse mAb - Loading Control
Catalog number :AT0003
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: microtubules, microfilaments (actin filaments), and intermediate filaments. Globular tubulin subunits comprise the microtubule building block, with α/β-tubulin heterodimers forming the tubulin subunit common to all eukaryotic cells. γ-tubulin is required to nucleate polymerization of tubulin subunits to form microtubule polymers. Many cell movements are mediated by microtubule action, including the beating of cilia and flagella, cytoplasmic transport of membrane vesicles, chromosome alignment during meiosis/mitosis, and nerve-cell axon migration. These movements result from competitive microtubule polymerization and depolymerization or through the actions of microtubule motor proteins.
- Overview
- Description
- Mouse monoclonal antibody to β-Tubulin - Loading Control
- Reactivity
- Human, mouse, rat, rabbit, monkey, cow, hamster.
- Tested applications
- WB : 1/2000-1/10000. Predicted molecular weight: 55 kDa.Not yet tested in other applications. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- Product Picture

- Specificity
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of beta Tubulin.
- Properties
- Immunogen
- a synthetic peptide corresponding to the amino terminus of human β-tubulin.
- Clonality
- Monoclonal, clone number: 6C4
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1
- Form
- Liquid, 100 μg at 1mg/mL
Mouse monoclonal immunoglobulin in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.3 (+/- 0.1), 50% glycerol with 0.1mg/mL BSA (IgG, protease free) as a stabilizer and 0.02% sodium azide as preservative.
- Storage instruction
- Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Aliquot and store at -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycle.
- Database links
- SwissProt: P07437 HumanSwissProt: P99024 MouseSwissProt: P69897 Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Applications
- WB Image
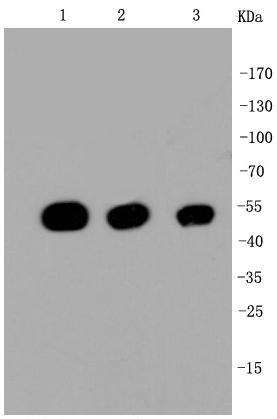
Western blot shows lysates of human brain (cerebellum) tissue, human brain (hypothalamus) tissue, mouse brain (cerebellum) tissue, and mouse brain (stem) tissue. A specific band was detected for beta Tubulin at approximately 55 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions.
- WB Figure 2

Western blot shows lysates of human brain (cerebellum) tissue, human brain (hypothalamus) tissue, mouse brain (cerebellum) tissue, and mouse brain (stem) tissue. A specific band was detected for beta Tubulin at approximately 55 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions.Recommended secondary antibody: Goat anti mouse IgG-HRP (Engibody, Catalog number:AT0098)
Recommended ECL: ECL Pico-Detect™ Western Chemiluminescent HRP Substrate (Engibody, Catalog number: IF6747)
- Protocols
- Western Blotting Procedure1. Lyse approximately 107 cells in 0.5 mL of ice-cold Cell Lysis Buffer (formulation provided below). This buffer, a modified RIPA buffer, is suitable for recovery of most proteins, including membrane receptors, cytoskeletal-associated proteins, and soluble proteins. This cell lysis buffer formulation is available as a separate product which requires supplementation with protease inhibitors immediately prior to use (Cat. # FNN0011, thermofisher). Other cell lysis buffer formulations, such as Laemmli sample buffer and Triton-X 100 buffer, are also compatible with this procedure. Additional optimization of the cell stimulation protocol and cell lysis procedure may be required for each specific application.2. Remove the cellular debris by centrifuging the lysates at 14,000 x g for 10 minutes. Alternatively, lysates may be ultra-centrifuged at 100,000 x g for 30 minutes for greater clarification.3. Carefully decant the clarified cell lysates into clean tubes and determine the protein concentration using a suitable method, such as the Bradford assay. Polypropylene tubes are recommended for storing cell lysates.4. React an aliquot of the lysate with an equal volume of 2x Laemmli Sample Buffer (125 mM Tris, pH 6.8, 10% glycerol, 10% SDS, 0.006% bromophenol blue, and 130 mM dithiothreitol [DTT]) and boil the mixture for 90 seconds at 100°C.5. Load 10-30 µg of the cell lysate into the wells of an appropriate single percentage or gradient mini-gel and resolve the proteins by SDS-PAGE.6. In preparation for the Western transfer, cut a piece of PVDF slightly larger than the gel. Soak the membrane in methanol for 1 minute, then rinse with ddH2O for 5 minutes. Alternatively, nitrocellulose may be used.7. Soak the membrane, 2 pieces of Whatman paper, and Western apparatus sponges in transfer buffer (formulation provided below) for 2 minutes.8. Assemble the gel and membrane into the sandwich apparatus.9. Transfer the proteins at 140 mA for 6°C 0-90 minutes at room temperature.10. Following the transfer, rinse the membrane with Tris buffered saline for 2 minutes.11. Block the membrane with blocking buffer (formulation provided below) overnight at 4°C or for one hour at room temperature.12. Incubate the blocked blot with primary antibody at a 1:1000 starting dilution in Tris buffered saline supplemented with 1% Ig-free BSA and 0.1% Tween-20 overnight at 4°C or for two hours at room temperature.13. Wash the blot with several changes of Tris buffered saline supplemented with 0.1% Tween 20.14. Detect the primary antibody band using an appropriate secondary antibody, such as goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated HRP (Cat. # AT0097-100ul, Engibody) or goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated HRP (Cat. # AT0098-100ul, Engibody) in conjunction with your chemiluminescence reagents and instrumentation.
- Troubleshooting Guide
- Western Blot Troubleshooting1. No signal2. High background3. Non specific bands4. Incorrect band size5. White bands on black/grey blot6. ‘Smear’1. Troubleshooting: NO SIGNALSample preparation• Untested species? Positive control. Check alignment.• Not enough antigen in the sample or loaded onto the gel.Transfer to the membrane• Poor transfer to membrane.• Excessive washing.Blocking• Too much blocking. Optimize blocking agent, concentration and time• Cross-reaction blocking agent / antibody.Antibody incubation and detection• Not enough antibody.• Incorrect secondary antibody.• Detection kit is old - substrate inactive.2. Troubleshooting: HIGH BACKGROUNDTransfer to the membrane• Choice of membrane.Blocking• Need to block for longer.• Optimize blocking agent, concentration.• Cross-reaction between blocking agent and primary or secondary.• Phospho-specific proteins: use Casein to block.Antibody incubation and detection• Primary antibody concentration too high.• Incubation temperature too high.3. Troubleshooting: NON SPECIFIC BANDSSample preparation• Cell lines can accumulate differences in their protein expression profiles.• Protein has multiple modified forms, altering mobility.• Target protein is in fragments – degradation by proteases or cleaved.• Splice variants / isoforms or possibly proteins from the same family.• Multimers (dimers) of protein (reduce and denature).• Bands may be non-specific. Run a no primary controlBlocking• Insufficient blocking. Optimizing concentration, time.Antibody incubation and detection• Primary or secondary antibody concentration too high.• Antibody has not been purified.4. Troubleshooting: INCORRECT BAND SIZESample preparation• Ensure sample is reduced and denatured unless stated otherwise on the datasheet.• Check for isoforms.• Is the sample a recombinant fragment? These will run at a different size.5. Troubleshooting: WHITE BANDS/ BLACK BLOT• Too much primary and/or too much secondary antibody.6. Troubleshooting: ‘Smear’• Overloading, Protein degradation.
Related Products
| Catalog number | AT0002 |
| Catalog number | AT0001 |
| Catalog number | AT0050 |
| Catalog number | AT0004 |
| Catalog number | AT0008 |
| Catalog number | AT0544 |
| Catalog number | AT0014 |
| Catalog number | AT0007 |
| Catalog number | AT0009 |
| Catalog number | AT0010 |
| Catalog number | AT0011 |
| Catalog number | AT0012 |
Reviews
loading...