Step 1: Preparation of DNA Template
Linearized plasmids or PCR amplification products with T7 promoter can be used as in vitro transcription templates, which can be dissolved in TE buffer or Nuclease Free Water.
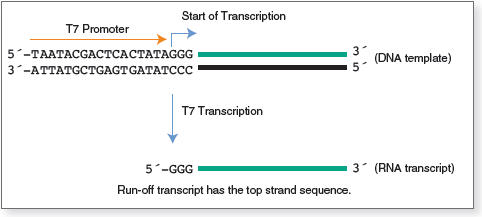
T7 promoter sequence: TAATACGACTCACTATAN*
Note: N * is the first base of RNA transcription, usually G.
(1) Plasmid template
Insert the target DNA into a plasmid vector containing the T7 promoter, then treat it with restriction enzymes and purify it after complete linearization.
Note 1: As terminators cannot guarantee 100% termination of transcription, circular plasmids will transcribe RNA products of different lengths. In order to obtain RNA of a specific length, plasmids must be fully linearized.
Note 2: The restriction enzyme selected for plasmid linearization needs to have a cleavage site immediately downstream of the coding chain and no recognition site in the coding chain. The selected restriction enzyme should be able to form a 5 'protruding end or a smooth end.
Note 3: In order to avoid the influence of proteins and salt ions on the transcription system, it is recommended to purify the linearized plasmid before using it as a template for in vitro transcription.
Note 4: The residual RNase A introduced during plasmid DNA extraction can significantly affect the quality of transcribed RNA. It is recommended to use high-purity RNase free templates with A260/A280 ratios of 1.8-2.0.
(2) PCR product template
The PCR product with T7 promoter can serve as an in vitro transcription template. Firstly, the T7 promoter sequence is added to the 5 'end of the primer upstream of the coding chain, and then the DNA template containing the T7 promoter is amplified under the action of high fidelity enzyme, followed by transcription. PCR products can be used as templates without purification, but the RNA yield will be higher after purification.
Note 1: PCR products used as templates must be confirmed for their specificity and concentration by electrophoresis. It is recommended to add 2-5 µL of PCR product to the 20 µL reaction system.
Note 2: In order to obtain more high-quality RNA, it is recommended to purify the PCR product before using it as a template for in vitro transcription.
Step 2: in vitro transcription
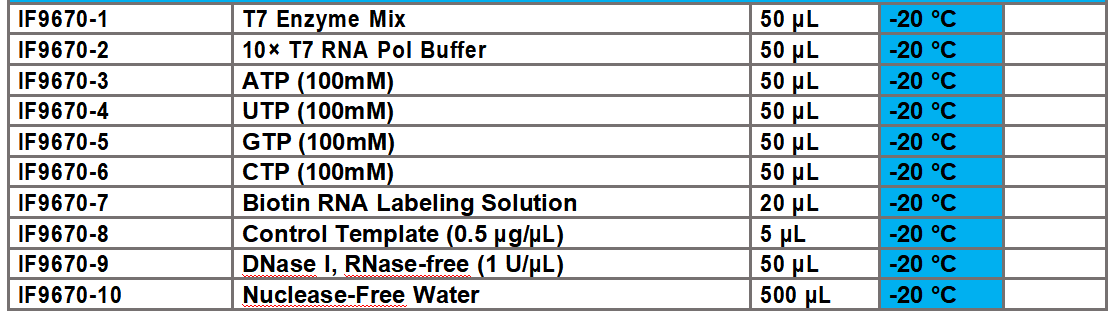
2.1 Preparation of T7 in vitro transcription and biotin labeling reaction system
Note 1: The transcription efficiency of different template sequences varies greatly. For the initial experiment, the recommended amount can be added first, and then the optimal system can be explored and optimized. The template amount can be adjusted within the range of 0.5 µg~2 µg.
As shown in the following figure:

2.2. After thorough mixing and instant separation, incubate at 37° C for 2 hours. If the length of the transcript is less than 100 nt, the reaction time can be extended to 3-16 h.
2.3 After the reaction is complete, add 2 µL DNase I per µg Template DNA to the product and incubate at 37° C for 15 minutes to remove the DNA template.
2.4. It is recommended to use hydroxymagnetic beads or column purification for transcribed RNA, or phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol purification can be used. The purified RNA can be used for downstream experiments or stored at -80° C for future use.
Step 3: Transcription of reference template
The control template is a linear DNA fragment containing the T7 promoter, with a transcript size of approximately 4000 nt. In the recommended in vitro transcription reaction system, at least 150 µ g of RNA can be obtained by reacting 1 µ g of control template DNA at 37° C for 2 hours.
Step 4: Product purification
The transcribed RNA can be purified using magnetic bead method, column purification or phenol chloroform isoamyl alcohol purification method to remove proteins and free nucleotides. The purified RNA can be subjected to downstream experiments or stored at -80° C after electrophoresis detection.
(1) Magnetic bead purification method
Follow the instructions for magnetic bead purification.
(2) Column purification method
Dilute the product to 100 µL by adding 80 µL of Nuclease Free Water before purification, and then follow the purification column instructions for purification.
(3) Purification by phenol chloroform isoamyl alcohol purification method
A. Add 115 µL of Nuclease Free Water and 15 µL of 3M sodium acetate (pH=5.2) to 20 µL of the reaction mixture and mix well.
B. Add an equal volume (150 µL) of phenol/chloroform (1:1) mixture for extraction, centrifuge at maximum speed (≥ 12000 rpm) for 5 minutes at room temperature, and transfer the upper aqueous solution to a new RNase free EP tube.
Note: Do not inhale the intermediate layer when transferring the supernatant.
C. Add an equal volume of chloroform for extraction twice, collect the supernatant, and transfer it to a new RNase free EP tube.
D. Add 2 times the volume of anhydrous ethanol to precipitate RNA. After mixing evenly, place at -20 ° C for at least 30 minutes, centrifuge at maximum speed (≥ 12000 rpm) at 4 ° C for 15 minutes, and collect the precipitate.
E. Add 500 µL of ice pre cooled 70% ethanol to wash the RNA precipitate, centrifuge at 4 ° C for 5 minutes at maximum speed (≥ 12000 rpm), and collect the precipitate.
F. Dissolve RNA precipitate in 20 µL of Nuclease Free Water. The purified RNA solution was stored at -80 ° C.
Step 5: RNA quantification
(1) NanoDrop method: Free NTP can seriously affect the accuracy of quantification, and RNA purification must be performed before using this method.
(2) Dye method (Qubit 4): RNA quantification can be performed using RNA specific fluorescent dyes or related reagent kits, which can quantify RNA in purified or unpurified reaction products.
Step 6: RNA detection
(1) Gel electrophoresis
In order to evaluate the length and quality of transcripts, appropriate non denatured or denatured agarose or polyacrylamide gel should be selected for electrophoretic detection of transcripts. Under denaturing electrophoresis, the formation of secondary structures in RNA can be reduced, which usually better reflects the migration of RNA with the correct molecular weight and size bands.
(2) Capillary electrophoresis method
Capillary electrophoresis can digitally and accurately evaluate the integrity, purity, or degradation degree of RNA samples. Compared with gel method, this method requires less RNA samples and has high sensitivity.
You can use Agilent's Bioanalyzer 2100 or Qsep100